Bangladesh is a developing country with a rapidly growing population. The current population of Bangladesh is 169.4 million as of 2023, based on Worldometer elaboration of the latest United Nations data. [1] Along with the increase in population, the energy demand of this country is increasing on the one hand, as well as the burning of oil, gas, and coal for the production of additional energy, the environment here has taken a very terrible picture. Especially Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, is under the most pressure from this increased population.
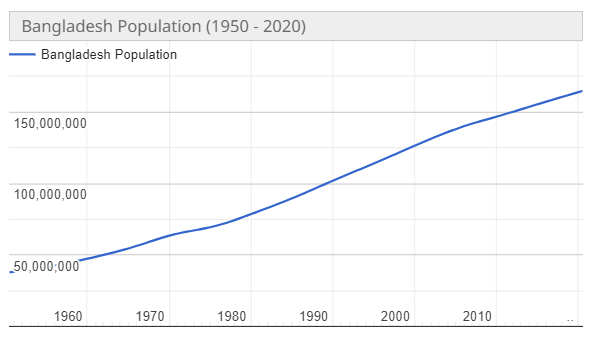
This population requires a significant amount of energy to sustain its economy and meet the energy demands of the people of Bangladesh.
Bangladesh has made significant progress in the electrification of its population and the expansion of its power generation capacity in recent years. However, the electrical energy scenario in Bangladesh still faces several challenges. Here are some key points:
- Access to electricity: Despite significant progress, access to electricity in Bangladesh is still limited, particularly in rural areas. According to World Bank data, as of 2020, only around 96.2% of the population had access to electricity. [2]
- Power generation capacity: Bangladesh has a total installed power generation capacity of around 25.284 GW in 2022, [3] with the majority of this capacity being provided by natural gas-fired power plants. The government has also made efforts to diversify the country’s energy mix, with an increasing focus on renewable energy sources such as solar and wind.
- Power generation infrastructure: The power generation infrastructure in Bangladesh is often criticized for being outdated and inefficient, leading to frequent power outages and supply disruptions.
- Energy security: Bangladesh is highly dependent on imports for its energy needs, which raises concerns about energy security. The country is working to increase domestic production of natural gas and has also made efforts to develop renewable energy sources.
- Power sector reform: The government of Bangladesh has undertaken a number of reforms aimed at improving the efficiency and sustainability of the power sector. These reforms include the establishment of an independent regulatory agency and the introduction of competitive bidding for power generation projects.
Overall, while Bangladesh has made progress in electrifying its population and expanding its power generation capacity, there is still much work to be done to ensure a stable and reliable supply of electrical energy for all its citizens.
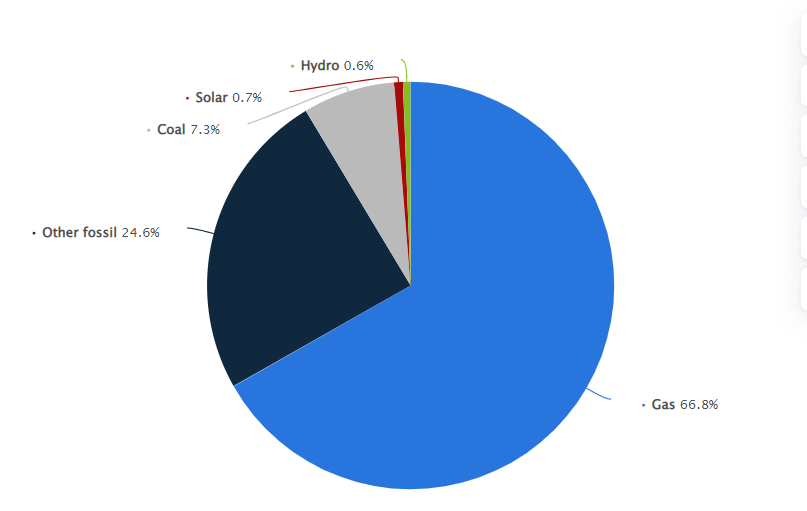
As the energy sector in Bangladesh is dominated by fossil fuels, specifically natural gas, coal, and furnace oil, which account for the majority of the energy mix, the country is slowly transitioning towards renewable energy sources, such as solar, hydro, and wind, to address its energy needs and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. But here is no geothermal resource to mention.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is the primary energy source in Bangladesh, accounting for over 66.8% of the country’s energy mix. [4] The country has significant reserves of natural gas, which are mostly located offshore in the Bay of Bengal. In recent years, the government has increased investment in the natural gas sector to meet the growing energy demands of the country. The natural gas industry in Bangladesh is dominated by the state-owned company, Petrobangla, which is responsible for the exploration, production, transportation, and distribution of natural gas.
Despite the vast reserves of natural gas in Bangladesh, the country faces several challenges in the sector. One of the major challenges is the insufficient infrastructure to transport and distribute natural gas, which leads to shortages in rural areas and industries. In addition, the country is facing declining production from its existing gas fields, which has led to a decrease in the supply of natural gas. To overcome these challenges, the government has implemented several measures, including the development of new gas fields and the construction of new pipelines.
Coal
Coal is another significant source of energy in Bangladesh, accounting for around 7.3% of the energy mix. [4] The country has limited coal reserves and relies on imports to meet its coal demand. The coal industry in Bangladesh is dominated by the state-owned company, Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB), which is responsible for the generation and distribution of electricity from coal-fired power plants.
Despite its limited reserves, the government is investing in the coal sector to meet the increasing energy demands of the country. Several coal-fired power plants are under construction or in the planning stages, which are expected to increase the coal-based generation capacity in the coming years. However, the use of coal as an energy source is facing opposition from environmental groups due to the negative impacts of coal on the environment, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Furnace oil
According to the Power Development Board’s estimates, gas fuels 50.84 percent of the total power generation, furnace oil 28 percent and diesel 6 percent, while coal-fired plants produce 7.89 percent of the country’s electricity. The new energy-saving policy is likely to create a shortfall of around 1,500 megawatts of power a day. [5] Furnace oil is mostly used for industrial and commercial purposes, and the country relies on imports to meet its furnace oil demand. The furnace oil industry in Bangladesh is dominated by the state-owned company, Bangladesh Oil, Gas and Mineral Corporation (PETROBANGLA), which is responsible for the import, storage, and distribution of furnace oil.
Despite its importance as an energy source, furnace oil is facing several challenges in Bangladesh. One of the major challenges is the high cost of furnace oil, which is affecting the competitiveness of the country’s industrial and commercial sectors. In addition, the use of furnace oil is contributing to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which are causing negative impacts on the environment and public health. To overcome these challenges, the government is promoting the use of alternative energy sources, such as natural gas and renewable energy, in the industrial and commercial sectors.
Diesel
Diesel is another significant source of energy in Bangladesh, accounting for around 6% of the energy mix. [5] Diesel is mainly used for transportation and for powering generators. The diesel industry in Bangladesh is dominated by private sector companies, which are responsible for importing, storing, and distributing diesel.
Solar
Solar energy has become an increasingly important source of energy in Bangladesh, and the country has great potential for future growth in this area. Here are some key points:
- Current usage of solar energy: Bangladesh has made significant investments in the development of solar energy in recent years. As of 2021, the country has a total installed capacity of around 1 GW, with much of this capacity being used for residential and commercial purposes. The government has also established several large-scale solar power projects, including the country’s first solar park. [6]
- Potential for future growth: Bangladesh has enormous potential for the growth of solar energy due to its high levels of solar insolation and relatively low investment costs compared to other forms of energy. The government has set ambitious targets to increase the country’s solar power capacity to 5 GW by 2041.
- Off-grid solutions: Bangladesh’s rural areas are often not connected to the national grid, which makes it difficult for many people to access electricity. Off-grid solar solutions such as solar home systems and community solar mini-grids have emerged as a promising solution for providing access to electricity in these areas.
- Promoting solar energy: The government of Bangladesh has taken a number of measures to promote the development of solar energy, including the introduction of tax incentives and subsidies for solar power projects, as well as the establishment of a dedicated agency to oversee the development of renewable energy in the country.
Overall, solar energy has a bright future in Bangladesh, with significant potential for future growth and the potential to play a key role in providing access to electricity for the country’s rural populations.

The government’s commitment to promoting renewable energy and increasing the country’s solar power capacity is an important step towards a more sustainable energy future.
Hydro
Hydroelectricity has the potential to play a significant role in meeting Bangladesh’s energy needs, although the country’s current capacity for hydroelectric generation is limited. There are the lowest per unit cost of production of electricity using hydro.
Hydroelectricity currently makes up a relatively small proportion of Bangladesh’s total power generation capacity, with most of the country’s electricity being generated from natural gas-fired power plants.
The government of Bangladesh has taken steps to promote the development of hydroelectric power, including the establishment of a dedicated agency to oversee the development of renewable energy in the country. The government has also introduced a number of incentives and subsidies for hydroelectric power projects, in an effort to encourage investment in this sector.
While the development of hydroelectric power in Bangladesh is facing a number of challenges, there is significant potential for the growth of this sector in the future.
Wind
Wind energy usage in Bangladesh is still in the early stages of development, with a limited amount of wind power currently being generated in the country.
As of 2023, the total installed capacity of wind power in Bangladesh is approximately 359.9 MW, with most of this capacity being generated by a few large-scale wind power projects. [7] There is also a small amount of wind power generated by off-grid wind turbines, particularly in rural areas.
Bangladesh has significant potential for the development of wind energy, with several areas of the country that are well-suited to wind power generation. The government has set a target to increase the country’s wind power capacity to 1 GW by 2041.
Thinking about the environment and future sustainability, many young researchers in Bangladesh are researching hybrid power plants. We have seen several projects in this regard.
Recently I saw a 1 MW Solar-hydro hybrid power plant project in the Chittagong Hill Tracts. In this solar-hydro microgrid proposal, all the electricity needs of the residents will be met by producing electricity through solar power plants in the daylight. Two types of arrangements were possible for the night. First of all, to store electricity from daytime solar power in a lead-acid battery and use it for the night. But in that case, these batteries had a serious impact on the environment. Considering the impact of environmental damage, novel initiatives have also been taken in this regard. As a lot of electricity can be produced from solar energy during the day, a portion of this product will be pumped to reserve the water tank. At night when there is no sunlight, this water will be used to generate hydropower. As a result, these hilly people will get uninterrupted electricity. It will also be one of the steps towards clean, reliable, long-term use of electricity.
In this way, the researchers have experimentally implemented a solar-hydro power plant of about 1 MW. With this successful project providing grid-quality AC power to around 100 households including shops, schools, community clinics, Kyang (pagodas), mosques, churches, and temples in the Bandarban region, the research team hopes to expand further in future years.
References




I was very pleased to uncover this great site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely appreciated every bit of it and I have you bookmarked to look at new information on your blog.